This is the world's first industry standard to assure a photo’s authenticity
The likes of Adobe, the BBC and Microsoft have formed an alliance and set a standard to verify online photos

Earlier last year, a coalition was formed between technology and media entities such as Adobe, Arm, BBC, Intel, Microsoft and Truepic to combat the spread of misinformation and build trust in verifying online content.
This joint Development Foundation project, known as The Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA), has managed to develop an end-to-end, open standard for tracing the origin and evolution of digital content.
• Read more: Best VPN for photographers
The C2PA has now released the first-ever technical specifications designed to certify a source, as well as the history of digital media. These specifications are the first of their kind, and will empower content creators and editors to develop tamper-evident media, enabling them to selectively disclose information about how their digital content has been initially created and further altered.
The goal of the C2PA since its formation has been to address the prevalence of disinformation and online content fraud, through developing technical standards for certifying the source and history or provenance of media content.

Some may wonder if this coalition is really necessary; with photo editors such as Photoshop and Lightroom being so popular among photographers, why has Adobe backtracked in a sense and is now fighting the upload of edited images?
In October 2021, Adobe built a new feature into Photoshop called Content Credentials, enabling creators to attach attribution data to images before sharing them online.
Get the Digital Camera World Newsletter
The best camera deals, reviews, product advice, and unmissable photography news, direct to your inbox!
This news came following the setup of The Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI) that was founded by Adobe, Twitter, and the New York Times in 2019, as a means to fight image disinformation by increasing the trust and transparency of content shared online. The CAI has since expanded and now includes support from Nikon, too.
This foundation of misinformation goes far beyond changing a few tones using the histogram or adjusting exposure to perfect your photographs. Heavily manipulated images and filters can be dangerous when used in the context of news and especially social media, in regard to influencer culture and promoting something that may not be entirely truthful.
Other applications of images that can cause harm to others include things like catfishing (using fake or stolen photos to court potential partners), fraud, deepfakes, fake profiles, deceitful evidence submitted to news outlets… you get the idea.
In the first paragraph overview section of the technical specification, it states: "We are witnessing extraordinary challenges to trust in media. As social platforms amplify the reach and influence of certain content via ever more complex and opaque algorithms, mis-attributed and mis-contextualized content spreads quickly. Whether inadvertent misinformation or deliberate deception via disinformation, inauthentic content is on the rise".
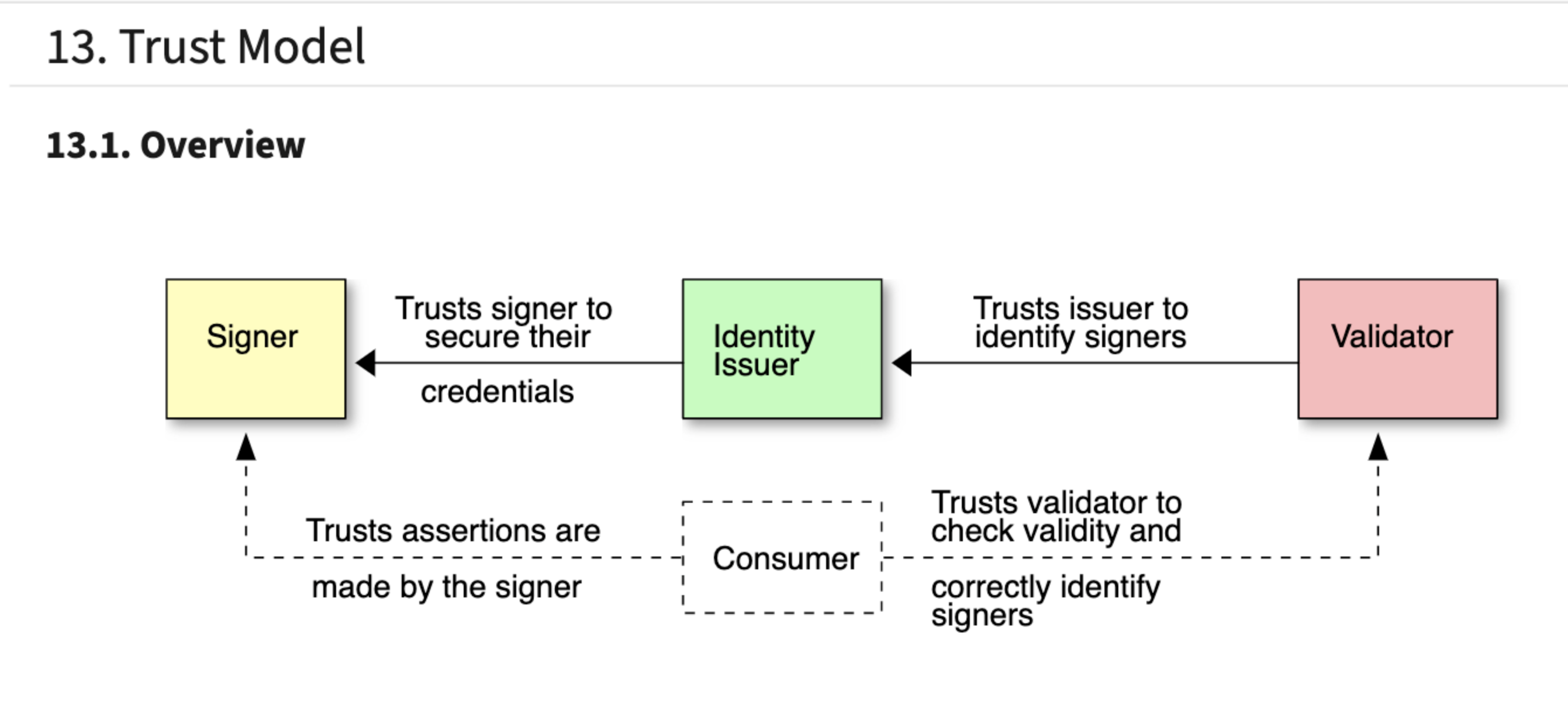
The specification describes the technical aspects of the C2PA architecture; a model for storing and accessing cryptographically verifiable information whose trustworthiness can be assessed based on a defined trust model, as shown via a diagram. The trust model features three entities specified in different colors; a consumer is expected to use the identity of the signer along with other trust signals, to decide whether the assertions made about an asset are true.
The schematics and specifications get more complicated as the contents unveil, but you can check out the specification standard for assuring content authenticity on the official C2PA website.
Read more:
Adobe Photoshop CC review
Adobe Lightroom CC review
Adobe Lightroom Classic review

Beth kicked off her journalistic career as a staff writer here at Digital Camera World, but has since moved over to our sister site Creative Bloq, where she covers all things tech, gaming, photography, and 3D printing. With a degree in Music Journalism and a Master's degree in Photography, Beth knows a thing or two about cameras – and you'll most likely find her photographing local gigs under the alias Bethshootsbands. She also dabbles in cosplay photography, bringing comic book fantasies to life, and uses a Canon 5DS and Sony A7III as her go-to setup.
