Cheat sheet: Rear curtain flash – how it works and why you need it
Your camera is set to 'front curtain' flash by default, but sometimes you need 'rear curtain' flash instead. Here's why
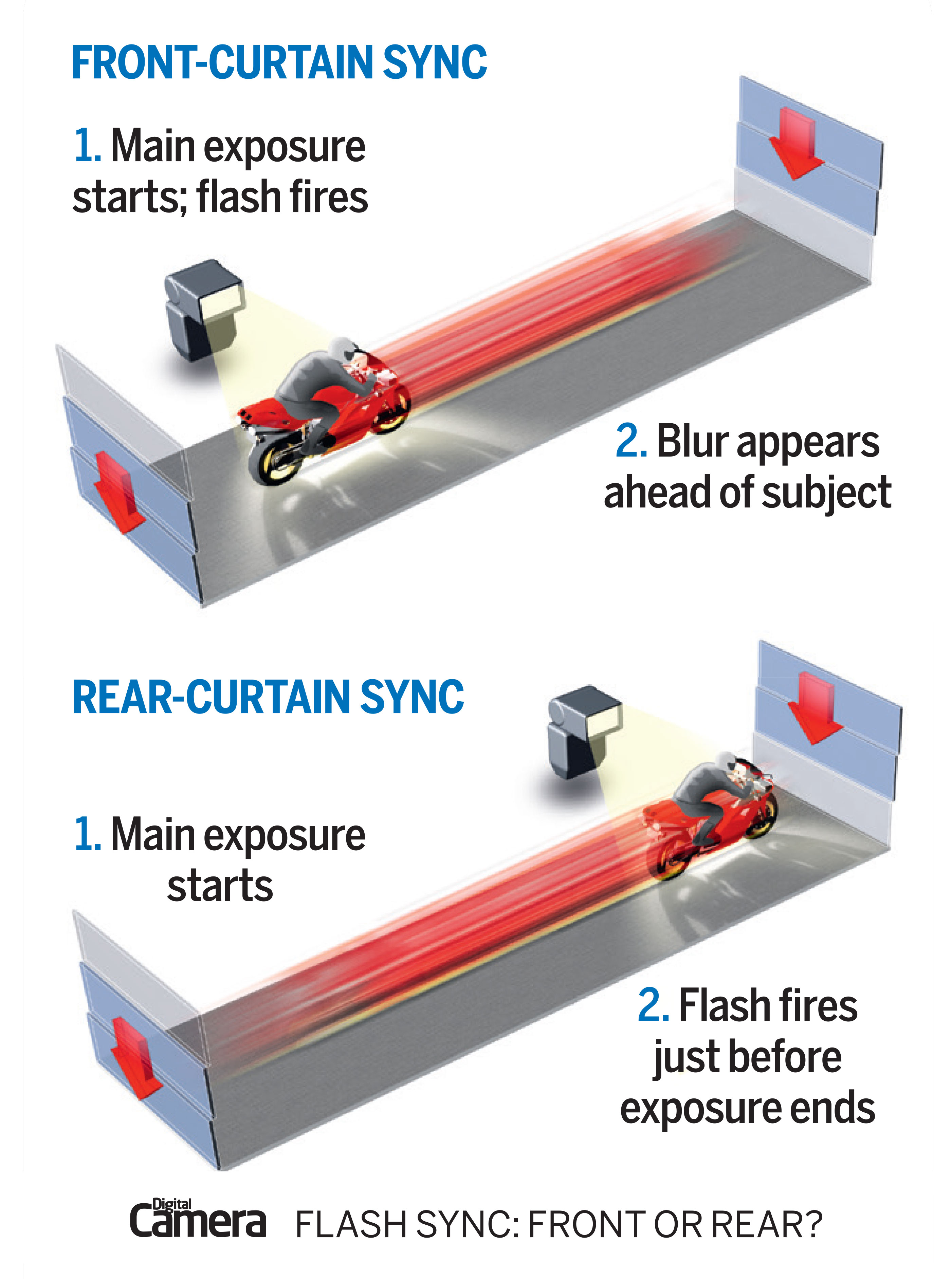
What is front and rear sync?
Flashguns produce a very short, intense burst of light. The flash 'duration' is very short, typically 1/500sec or even 1/1000sec, even though you will usually be working with much slower shutter speeds, and hence longer exposures, than that.
This means you have a choice about when the flash fires during the exposure – at the start (first-curtain sync) or at the end (rear-curtain sync). The 'curtain' is part of the focal plane shutter design of DSLRs and mirrorless cameras. The first curtain of the shutter moves aside to expose the sensor, the second moves across an instant later to cover it up again.
Front- or first-curtain sync
By default, a flash fires when the shutter curtains open to expose the camera sensor to light, enabling you to time shots to perfection. The flash is providing the main illumination and will fire the instant you press the shutter release.
Knowing exactly when the flash will fire is important, which is why this is the default flash mode setting.
However, if you are using slow-sync flash technique to combine the 'freezing' effect of flash and the existing ambient light, you will need to extend the eposure to record that dimmer background lighting. If you do this with a moving subject you will get an. odd effect where the blur trail of the subject is in front of it, not behind it, which is not what we expect motion blur to look like.
Rear- or second-curtain sync
In this mode, the flash fires at the end of the main exposure, not at the start. Any motion blur recorded at the start of the exposure will now trail behind the subject, creating a more natural result.
However, this makes timing your shots more difficult because you have to gauge where your subject will be in the frame at the end of the exposure. With this technique, it's easy to mis-time it and have your subject exiting the frame before the flash fires.

So which sync mode is best?
For regular flash photography and when you're not trying to capture movement blur in your subject, the default front- or first-curtain sync mode is best. It's easier to time your shots and you can still balance flash with ambient light.
The effects of rear-curtain sync flash are only obvious at slower shutter speeds and when you want to capture moving subjects both sharply (with the flash) and as a blur trail (with a longer exposure). Try using it at night when shooting cars: the trails created by the headlights will add a real sense of speed.
Read more:
• Best flashguns
• What is flash and is it still useful?
• Get more from your flash
Get the Digital Camera World Newsletter
The best camera deals, reviews, product advice, and unmissable photography news, direct to your inbox!

Rod is an independent photography journalist and editor, and a long-standing Digital Camera World contributor, having previously worked as DCW's Group Reviews editor. Before that he has been technique editor on N-Photo, Head of Testing for the photography division and Camera Channel editor on TechRadar, as well as contributing to many other publications. He has been writing about photography technique, photo editing and digital cameras since they first appeared, and before that began his career writing about film photography. He has used and reviewed practically every interchangeable lens camera launched in the past 20 years, from entry-level DSLRs to medium format cameras, together with lenses, tripods, gimbals, light meters, camera bags and more. Rod has his own camera gear blog at fotovolo.com but also writes about photo-editing applications and techniques at lifeafterphotoshop.com
